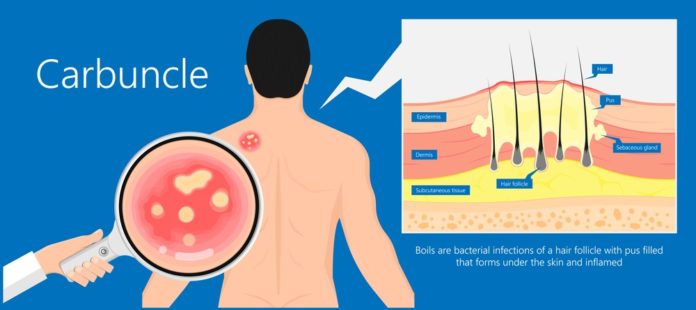
A carbuncle is a clump of reddish, swollen, and sensitive boils linked beneath the skin. A boil is a hair follicle condition characterised by a small collection of pus beneath the skin. A usually single carbuncle is most likely to appear on a hairy portion of the body, such as the back or scruff of the neck. However, carbuncles can appear in various body parts, including the buttocks, thighs, groyne, and armpits.
Carbuncles necessitate medical attention to limit or control complications, enhance healing, and prevent scarring. If you have a boil or boils present for more than a few days, consult your doctor.
Risk Factors for Carbuncles
Carbuncles are associated with advanced age, obesity, poor cleanliness, and poor general health. Other carbuncle risk factors include:
- Chronic skin conditions that compromise the skin’s protective barrier
- Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of people.
- Kidney failure
- The illness of the liver
- Any medical disease or therapy that compromises the immune system
Symptoms of Carbuncles
Typically, the boils that develop carbuncles begin as red, painful lumps. The carbuncle becomes clogged with pus and develops white or yellow points that leak, ooze, or crust. Many untreated carbuncles rupture over time, releasing a creamy white or pink fluid.
Other carbuncle symptoms include fever, exhaustion, and a general feeling of being sick. Swelling may occur in adjacent muscles and lymph nodes, particularly the neck, armpit, or groyne.
Medical Treatments for Carbuncles
If a boil or boils do not dry out and cure after a few days of home treatment, or if you are unsure whether you have a carbuncle, see your doctor. Also, seek medical attention if a carbuncle appears on your face, near your eyes or nose, or on your spine. Also, consult a doctor if you have a carbuncle that is huge or painful to convert.
Your doctor may cut and drain the carbuncle and clean the region with a sanitary solution to ensure that all of the fluid has been drained out.
Antibiotics usually are unnecessary if the carbuncle has been completely emptied. However, antibiotic treatment may be required in the following situations:
- When MRSA is present, and drainage is incomplete
- There is a soft-tissue infection in the surrounding area (cellulitis)
- A person’s immune system is compromised.
- An illness has spread to several regions of the body.
- Most carbuncles cure within two to three weeks of medical therapy, depending on severity.